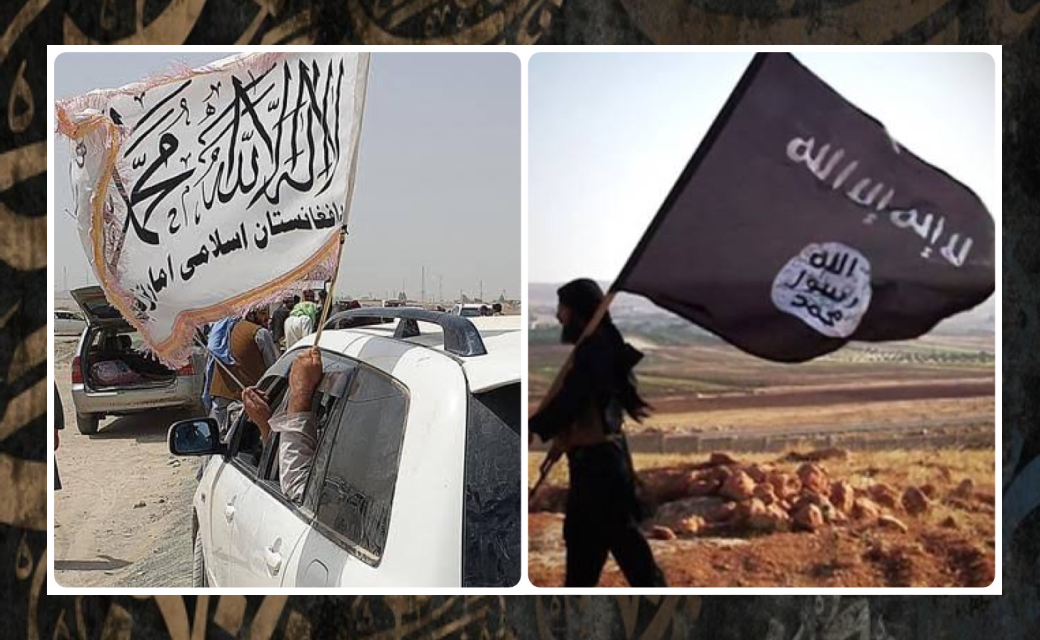
Who’s Who when it comes to ISIS, ISIL and the Taliban
The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) also known as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria(ISIS) officially known as the Islamic State (IS) and also known by its Arabic acronym Daesh داعش is a militant group that follows a Salafi jihadist doctrine which is ultimately an extremist group driven from minimal Islamic laws and instead majority man-made laws and regulations which do not have Islamic backing and hence should not represent the Islamic Ideology or Religion.
ISIL was founded by Abu Musab al-Zarqawi and gained global prominence in 2014. The group has been designated as a terrorist organization by the United Nations.In the same year it proclaimed itself a worldwide caliphate and began referring to itself as the Islamic State. As a caliphate, it claimed religious, political, and military authority over all Muslims worldwide. Its adoption of the name Islamic State and its idea of a caliphate have been criticized, with the United Nations, various governments, and mainstream Muslim groups rejecting its statehood. ISIL is believed to be operational in 18 countries, including Afghanistan and Pakistan. Many Taliban militants defected to join the Islamic State affiliate, and the two groups fight for resources and territory.
Their differences are also ideological, according to the Stanford center. “The hostility between the two groups arose both from ideological differences and competition for resources. IS accused the Taliban of drawing its legitimacy from a narrow ethnic and nationalistic base, rather than a universal Islamic creed,” the center said. Since its founding, the Islamic State affiliate has been at odds with the Taliban, which now control Afghanistan.
The Taliban differ from al-Qaeda as many of their principles stem from the traditional Pashtun tribal way of life in Afghanistan, although both practice branches of Salafi and Wahabi Sunni Islam ( a newly established sets of rules and regulations that are NOT aligned with Islam ). The group came to prominence in Afghanistan in the autumn of 1994, and governed in the country for five years, from 1996 to 2001. Taliban means ‘student’ in Arabic, and it is widely speculated that the group first emerged from religious seminaries which preached a strict variation of Sunni Islam. They originally promised to restore peace and security via Sharia law in the Pashtun areas of Pakistan and Afghanistan. However, the group enforces extremely strict laws by which its citizens must live. Women over the age of 10 are prohibited from receiving an education, and televisions and social media are banned, all of which have zero representation of the Islamic Law. Islam recommend for women, men and children to achieve highest levels of education and has no stance against presence or use of Social Media. Although Islam does recommends positive use of any available technology, social media included.
Commonality between ISIS, ISIL and Taliban
The main commonalities between all these groups are injection of fear into societies they encounter, terrorizing anyone and everyone who does not obey by their rules, and having zero tolerance for diversity. This by itself is a contradiction to the verse of Quran 49:13 which estates “O men! Behold, We have created you all out of a male and a female, and have made you into nations and tribes, so that you might come to know one another. Verily, the noblest of you in the sight of God is the one who is most deeply conscious of Him. Behold, God is all-knowing, all-aware.”
Islam is all welcoming, promotes diversity and inclusion, encourages achieving highest levels of education. Here are 10 inventions by Muslims throughout history. If Islam was opposed excellence, education or limited its people, non of the following life changing inventions would’ve been possible.
1. Surgery
Around the year 1,000, the celebrated doctor Al Zahrawi published a 1,500 page illustrated encyclopedia of surgery that was used in Europe as a medical reference for the next 500 years. Among his many inventions, Zahrawi discovered the use of dissolving cat gut to stitch wounds — beforehand a second surgery had to be performed to remove sutures. He also reportedly performed the first caesarean operation and created the first pair of forceps.
2. Coffee
Now the Western world’s drink du jour, coffee was first brewed in Yemen around the 9th century. In its earliest days, coffee helped Sufis stay up during late nights of devotion. Later brought to Cairo by a group of students, the coffee buzz soon caught on around the empire. By the 13th century it reached Turkey, but not until the 16th century did the beans start boiling in Europe, brought to Italy by a Venetian trader.
3. Flying machine
“Abbas ibn Firnas was the first person to make a real attempt to construct a flying machine and fly,” said Hassani. In the 9th century he designed a winged apparatus, roughly resembling a bird costume. In his most famous trial near Cordoba in Spain, Firnas flew upward for a few moments, before falling to the ground and partially breaking his back. His designs would undoubtedly have been an inspiration for famed Italian artist and inventor Leonardo da Vinci’s hundreds of years later, said Hassani.
4. University
In 859 a young princess named Fatima al-Firhi founded the first degree-granting university in Fez, Morocco. Her sister Miriam founded an adjacent mosque and together the complex became the al-Qarawiyyin Mosque and University. Still operating almost 1,200 years later, Hassani says he hopes the center will remind people that learning is at the core of the Islamic tradition and that the story of the al-Firhi sisters will inspire young Muslim women around the world today.
5. Algebra
The word algebra comes from the title of a Persian mathematician’s famous 9th century treatise “Kitab al-Jabr Wa l-Mugabala” which translates roughly as “The Book of Reasoning and Balancing.” Built on the roots of Greek and Hindu systems, the new algebraic order was a unifying system for rational numbers, irrational numbers and geometrical magnitudes. The same mathematician, Al-Khwarizmi, was also the first to introduce the concept of raising a number to a power.
6. Optics
“Many of the most important advances in the study of optics come from the Muslim world,” says Hassani. Around the year 1000 Ibn al-Haitham proved that humans see objects by light reflecting off of them and entering the eye, dismissing Euclid and Ptolemy’s theories that light was emitted from the eye itself. This great Muslim physicist also discovered the camera obscura phenomenon, which explains how the eye sees images upright due to the connection between the optic nerve and the brain.
7. Music
Muslim musicians have had a profound impact on Europe, dating back to Charlemagne tried to compete with the music of Baghdad and Cordoba, according to Hassani. Among many instruments that arrived in Europe through the Middle East are the lute and the rahab, an ancestor of the violin. Modern musical scales are also said to derive from the Arabic alphabet.
8. Toothbrush
According to Hassani, the Prophet Mohammed popularized the use of the first toothbrush in around 600. Using a twig from the Meswak tree, he cleaned his teeth and freshened his breath. Substances similar to Meswak are used in modern toothpaste.
9. The crank
Many of the basics of modern automatics were first put to use in the Muslim world, including the revolutionary crank-connecting rod system. By converting rotary motion to linear motion, the crank enables the lifting of heavy objects with relative ease. This technology, discovered by Al-Jazari in the 12th century, exploded across the globe, leading to everything from the bicycle to the internal combustion engine.
10. Hospitals
“Hospitals as we know them today, with wards and teaching centers, come from 9th century Egypt,” explained Hassani. The first such medical center was the Ahmad ibn Tulun Hospital, founded in 872 in Cairo. Tulun hospital provided free care for anyone who needed it — a policy based on the Muslim tradition of caring for all who are sick. From Cairo, such hospitals spread around the Muslim world.